Home physiotherapy plan for Erb's Palsy kids ( Physiotherapy home plan for brachial plexus injury child
Home physiotherapy (plan and advice )
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy should start soon after your baby has been diagnosed with having OBPP. Physiotherapy cannot make the nerves grow faster but aim to reduce the problems of stiffness occurring because your baby cannot move their arm by themselves. You will be instructed in a range of motion exercises, which will help to keep muscles and joints flexible and ready to move, if and when nerve and muscle function improves
The aims of physiotherapy are
to prevent stiffness developing in the joints of the affected arm;
to encourage your baby to move their arm; for you to be aware of reduced sensation
your baby may have, and how to increase their awareness of their arm;
to ensure that your baby reaches their developmental milestones at the right time.
A physiotherapy program may include
how to move your baby's arm to stop it from becoming stiff;
• how to move and handle your baby when caring for them;
positions to use for sleep and for play;
advice on activities to help with their development.
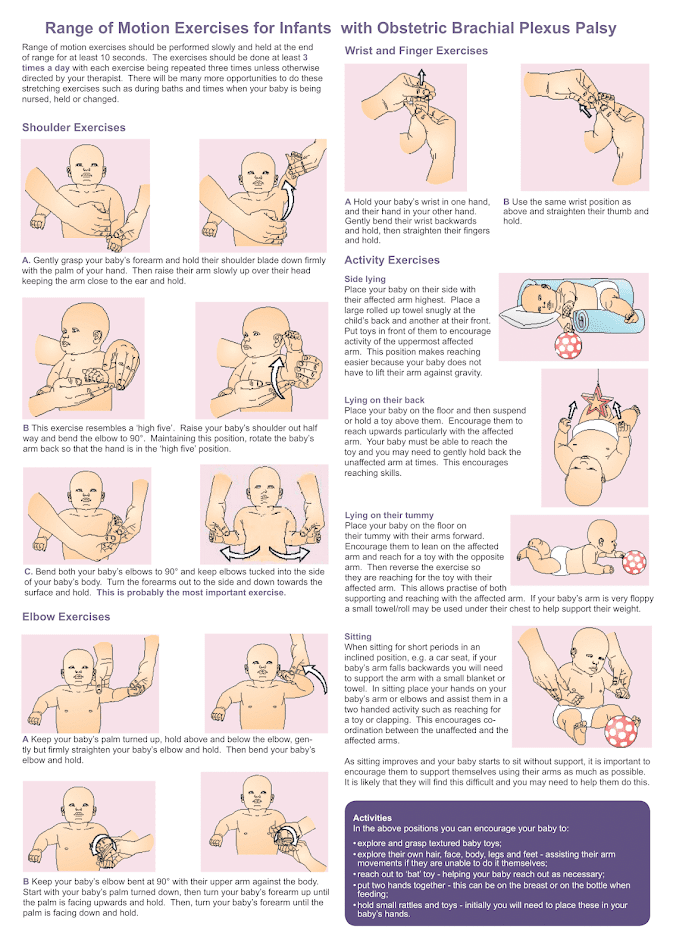
Range of motion exercises
Range of motion exercises are movements done with your baby's arm
ensure that the joints maintain full movement.
Positioning and handling
it is important to touch and to gently move your baby's arm;
do not pull on your baby's affected arm or lift under the armpits;
when handling, feeding, and cuddling your baby, the affected
the arm should be well supported close to their side or in a forward position;
move your baby's arm gently for washing, dressing, and skin
care - it is helpful to dress the affected arm first and undress it last and when washing and drying, particular care should be taken with skin folds;
if your baby's arm is very floppy it should be well supported with the hand, elbow, and shoulder in the neutral position - often a towel under the affected arm during
sleep helps to keep the arm in the neutral position;
Sensation
Your baby may have reduced sensation in their arm.
To increase your baby's body awareness you can:
• rest your baby’S hand on your breast/bottle during feeding;
rub a variety of textures against your baby's skin, e.g. velvet for soft sensations, a bath towel for rough ones;
gently stroke and massage;
bring your baby's hands to their mouths.
Some babies may not tolerate this because of increased sensitivity, but in others, it will increase the awareness of the affected arm.
Dr.Akshay Raj Chandra PT
Consultant pediatric
physiotherapist
www.physiohomebased.com
Comments