Frozen shoulder or Adhesi
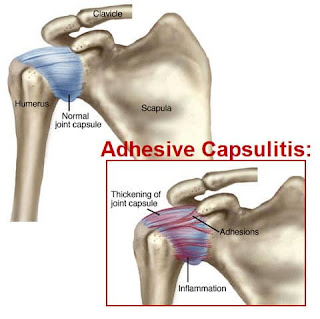
The term adhesive capsulitis implies that the shoulder joint capsule has adhesions and inflammation that limits the motion of the shoulder.
While this condition is common, its cause is not well understood. We do know, however, that this condition is more common in females than in males,
the non-dominate shoulder is more affected than the dominant shoulder, and the prevalence is more common after the age of 40.
It takes between six months and three years to stabilize and regress. Unfortunately, there is often a residual permanent reduction in shoulder motion.
Adhesions are fibrotic bands of scar tissue that join the surfaces of two anatomic surfaces. With time, adhesions tend to expand in breadth while they tighten and bind normal motion. The shoulder has a propensity for developing adhesions. If shoulder joint inflammation and fibrotic adhesions combine, the condition we know as a frozen shoulder develops.
Trauma
Tendinitis bursitis
Rotator cuff injury
Overuse of faulty movement
Poor sleeping posture
Non-shoulder’
Diabetes thyroid
Referred pain like(IHD ischemic heart disease )
Prolong use of a sling
muscle weakness
Signs and Symptoms of Fro
Decreased shoulder motion
Reduced arm swing while walking
Holding the arm in a protective manner near the body
Stooped rounded shoulders
Neck and back pain
stage of Frozen shoulder
Freezing, or painful stage:
Pain increases gradually, making shoulder motion harder and harder. Pain tends to be worse at
night. This stage can last from 6 weeks to 9 months.
Frozen:
Pain does not worsen, and it may decrease at this stage. The shoulder remains stiff. It can last from 4 to 6 months, and movement may be restricted.
Thawing:
Movement gets easier and may eventually return to normal. Pain may fade but occasionally recur. This takes between 6 months and 12 months
vicious_cycle_of_frozen_s
Repeated strain ------inflammation ----fibrosis-----thickness
Diagnosis :
diagnose of frozen shoulder based on signs, symptoms, and an examination, paying close attention to the arms
and shoulders.
PHYSICAL_EXAMINATION
>Structural problems can only be identified with the help of imaging tests,
such as an
X-ray or
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Prevention
Frozen shoulder can only be prevented if it is caused by an injury that makes shoulder movement difficult.
Anyone who experiences such an injury should talk to a doctor about exercises for maintaining mobility and flexibility of the shoulder joint.
Treatment
The aim is to alleviate pain and preserve mobility and flexibility in the shoulder. In time and with treatment
However, recovery may be slow, and symptoms can persist for several years.
There are several ways to relieve pain and alleviate the condition.
Painkillers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Physical therapy: This can provide training in exercises to maintain as much mobility and flexibility as possible without straining the shoulder or causing too much pain
PAIN CONTROL (the first aim of the therapist ) if required to give them NSAIDs it helps reduce inflammation and also help
in pain reduce
FUNCTIONAL RANGE OF MOTION
in case of pain and Inflammation ( Not to advise to do active movement it causes inflammation it may cause more pain
pendular exercise
GRADE 1 AND GRADE 2 MOBILIZATION
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE
ACTIVE EXERCISE
STRENGTHENING EXERCISE
ELECTROTHERAPY MODALITIES
The term adhesive capsulitis implies that the shoulder joint capsule has adhesions and inflammation that limits the motion of the shoulder.
While this condition is common, its cause is not well understood. We do know, however, that this condition is more common in females than in males,
the non-dominate shoulder is more affected than the dominant shoulder, and the prevalence is more common after the age of 40.
It takes between six months and three years to stabilize and regress. Unfortunately, there is often a residual permanent reduction in shoulder motion.
Adhesions are fibrotic bands of scar tissue that join the surfaces of two anatomic surfaces. With time, adhesions tend to expand in breadth while they tighten and bind normal motion. The shoulder has a propensity for developing adhesions. If shoulder joint inflammation and fibrotic adhesions combine, the condition we know as a frozen shoulder develops.
the exact cause adhesive capsulitis is not well known but few of them are the associated reason that causes
frozen shoulder such as
there are two types of cause shoulder related to cause and non-shoulder related cause
shoulder Related cause
frozen shoulder such as
there are two types of cause shoulder related to cause and non-shoulder related cause
shoulder Related cause
Trauma
Tendinitis bursitis
Rotator cuff injury
Overuse of faulty movement
Poor sleeping posture
Non-shoulder’
Diabetes thyroid
Referred pain like(IHD ischemic heart disease )
Prolong use of a sling
muscle weakness
Signs and Symptoms of Fro
Decreased shoulder motion
Reduced arm swing while walking
Holding the arm in a protective manner near the body
Stooped rounded shoulders
Neck and back pain
stage of Frozen shoulder
Freezing, or painful stage:
Pain increases gradually, making shoulder motion harder and harder. Pain tends to be worse at
night. This stage can last from 6 weeks to 9 months.
Frozen:
Pain does not worsen, and it may decrease at this stage. The shoulder remains stiff. It can last from 4 to 6 months, and movement may be restricted.
Thawing:
Movement gets easier and may eventually return to normal. Pain may fade but occasionally recur. This takes between 6 months and 12 months
vicious_cycle_of_frozen_s
Repeated strain ------inflammation ----fibrosis-----thickness
Diagnosis :
diagnose of frozen shoulder based on signs, symptoms, and an examination, paying close attention to the arms
and shoulders.
PHYSICAL_EXAMINATION
>Structural problems can only be identified with the help of imaging tests,
such as an
X-ray or
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Prevention
Frozen shoulder can only be prevented if it is caused by an injury that makes shoulder movement difficult.
Treatment
The aim is to alleviate pain and preserve mobility and flexibility in the shoulder. In time and with treatment
However, recovery may be slow, and symptoms can persist for several years.
There are several ways to relieve pain and alleviate the condition.
Painkillers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Physical therapy: This can provide training in exercises to maintain as much mobility and flexibility as possible without straining the shoulder or causing too much pain
PAIN CONTROL (the first aim of the therapist ) if required to give them NSAIDs it helps reduce inflammation and also help
in pain reduce
FUNCTIONAL RANGE OF MOTION
in case of pain and Inflammation ( Not to advise to do active movement it causes inflammation it may cause more pain
pendular exercise
GRADE 1 AND GRADE 2 MOBILIZATION
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE
ACTIVE EXERCISE
STRENGTHENING EXERCISE
ELECTROTHERAPY MODALITIES


Comments